Abstract
Background: Cytopenia has arisen as a common and potentially limiting side effect of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CART) therapy. Compared to CD19-CART, less information is available after B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) CART treatment for multiple myeloma (MM). Rejeski K. et al (Blood, 2021)1 designed the CAR-HEMATOTOX score as a risk-stratifying method to help anticipate outcomes and potentially apply prophylactic measures in lymphoma patients (pts). Our institution has developed an academic BCMA CART called ARI0002h which is being tested in the CARTBCMA-HCB-01 clinical trial for pts with relapsed/refractory MM (NCT04309981)2.
Methods: Data of 30 MM pts treated with ARI0002h were collected. Cytopenias were graded according to CTCAE v4.03. Neutrophil recovery phenotypes were established as defined previously1 with slight modifications to be adapted to our cohort behavior: (1) Quick recovery: sustained recovery within the first 56 days (d) without a second decrease, (2) Intermittent recovery: initial recovery to at least grade 2 and second drop, (3) Aplastic: maintained grades 3-4 neutropenia with delayed recovery from d56. Time-dependent variables such as duration of cytopenias were estimated using Kaplan-Meier or Cox regression.
Results: Main features of the pts, disease, response and survival data can be found elsewhere2. With a median age of 61 years (y) (IQR 53-66), median time from MM diagnosis to ARI0002h treatment was 4.7 y (IQR 3.7-9.1), with a median of 4 (IQR 3-5) previous lines including 87% and 13% of prior autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation. All pts had previous triple-exposure to bortezomib, lenalidomide and daratumumab, and 37% were penta-exposed (addition of carfilzomib and pomalidomide). Cytokine release syndrome was developed in 90% (all grades 1-2) of cases with a median time to onset of 8 d; no cases of neurotoxicity were noted.
The incidence of cytopenias were: neutropenia 100% (7% grade 3, 93% grade 4), thrombocytopenia 90% (30% grades 1-2, 30% grade 3, 30% grade 4) and anemia 90% (43% grades 1-2, 47% grades 3-4). Median time in months (m) to complete resolution of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and anemia was 4 (95% CI 3-5), 11.7 (95% CI 5.5-17.9) and 3.1 (95% CI 1-13.2), respectively. Median duration of grade 3 neutropenia correlated with the development of infections (p=0.019).
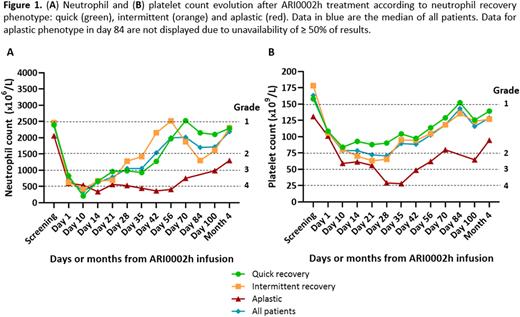
When analyzing the dynamics of cytopenias until month 4, we observed similarities and differences regarding those observed in CD19-CART. Thus, kinetic of neutrophil recovery was slower in this cohort. An improvement of the initial grade 4 neutropenia was seen starting between d14 and 21, but most pts remained in grades 3-4 neutropenia until d35 (68%) and 42 (50%) (Figure 1A). This difference in kinetics may be due the underlying disease and the latter onset of CRS observed in our cohort compared to lymphoma published data3-4. On the other hand, similar phenotypes were observed here: (1) Quick recovery in 41% (2) Intermittent recovery in 45%, developing a second drop from d56, and (3) Aplastic behavior in 14% (Figure 1A). Phenotype definitions were adapted due to the slower kinetics of recovery. Thus, phenotype 1 had a quick recovery but after d35, and pts with an intermittent behavior did not always reach neutrophils ≥ 1500, but ≥ 1000 before presenting a second drop.
Platelet recovery kinetics was similar to CD19-CART lymphoma pts. Interestingly, when analyzing platelet counts of pts according to the phenotype of neutropenia, no second drop was observed in Intermittent recovery phenotype, behaving as quick recovery pts, and aplastic pts had lower platelet counts over time compared to the other two phenotypes (Figure 1B).
We found a lack of association between baseline characteristics of pts, including age, previous lines of treatment or drug exposure, and the duration and severity of cytopenias; only serum C-reactive protein (CRP) at screening (p=0.044) and CRS duration (p=0.012) correlated with neutropenia duration. CAR-HEMATOTOX score did not discriminate two different subpopulations regarding severe neutropenia duration when applied to our cohort.
Conclusion: ARI0002h-related neutropenia is clinically relevant and has a slower recovery profile compared to CD19-CART therapy for lymphoma, but with three differentiated phenotypes with a similar clinical behavior. CRP level and CRS duration were the only variables associated with the duration of neutropenia.
Disclosures
Rodríguez-Otero:Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Sanofi: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Regeneron: Speakers Bureau. Zabaleta:Roche Glycart AG: Research Funding. Paiva:EngMab: Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb-Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Adaptive: Honoraria; GSK: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Oncopeptides: Honoraria. Juan:Gyala Therapeutics S.L.: Research Funding. Moraleda:Novartis, Gilead, Roche, Sanofi, Jazz, and Takeda.: Consultancy. Urbano-Ispizua:Miltenyi: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy. Mateos:Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen Cilag: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Fernandez de Larrea:Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; BeiGene: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal